Menu
Menu


Multimodal Artificial Intelligence approaches combine diverse data modalities, such as cancer multiomics (e.g., genomics, proteomics, metabolomics, radiomics), imaging, histopathology, clinical and biological data, and other real-world data, into unified analytical models (Figure 1).
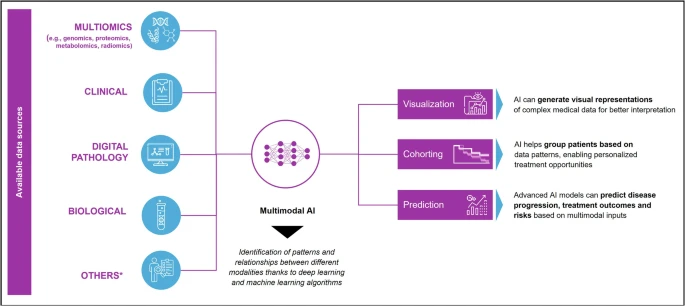
Unlike traditional single-biomarker approaches, MMAI captures relationships across biological and clinical scales, linking molecular changes to patient outcomes. This holistic approach enhances predictive accuracy, interpretability, and clinical utility, offering an unprecedented potential to transform every phase of cancer research and management.
By bridging the gap between biological complexity and computational capability, MMAI unlocks richer insights that can transform how prevention, diagnosis, treatment, and drug development are conducted, with implications for health economics, regulatory policy, and global health equity (Figure 2).
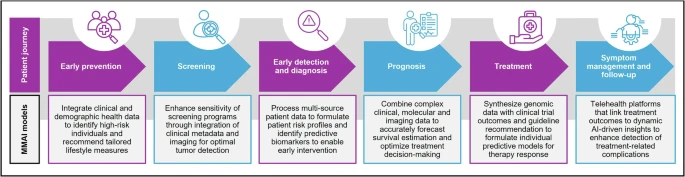
MMAI is emerging as a powerful tool for personalized prevention, and population-level screening by integrating clinical data to predict cancer risk and guide early interventions.
MMAI enables a shift from reactive to data-informed decision-making by synthetizing diverse data types into meaningful insights.
Precision oncology relies on accurately identifying meaningful patient subgroups. MMAI enables this by integrating hundreds of biological and clinical variables beyond the scope of traditional analytics.
MMAI is revolutionizing the entire drug development process, from discovery to development and clinical validation. Through smarter patient recruitment, synthetic control arms, and adaptive trial design, MMAI accelerates drug discovery and optimizes clinical trials, ultimately streamlining approvals and reducing costs.
It’s undeniable that MMAI brings measurable advantages for health systems struggling with the fast pace and rising oncology costs, by improving patient-therapy matching, reducing overtreatment, and shortening diagnostic times.
|

|

|
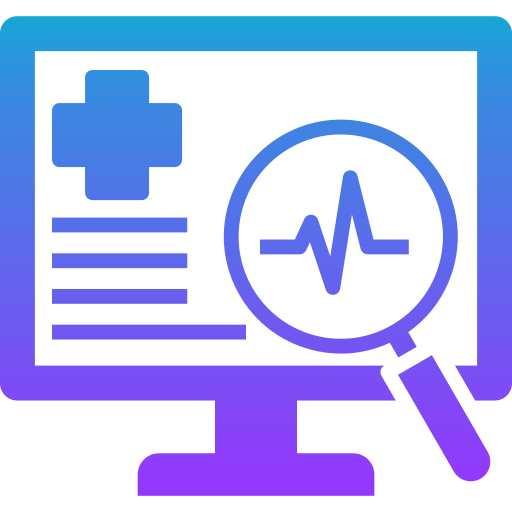
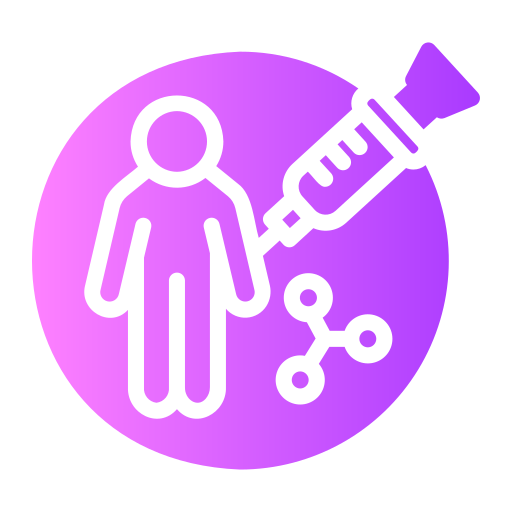
| Interoperable data results in system-level gains | Improved diagnostic capability reduces overtreatment | Diagnostics and targeted treatment shift to increased cost-effectiveness |
| Deploying MMAI on harmonized datasets (e.g., FHIR and OMOP frameworks) allows for multiple types of data to be analyzed together rather than in silos, reducing human burden and increasing productivity. | Combining digital pathology, multiomics and other clinical variables, MMAI can uncover biomarker signatures that identify optimal treatment responders, ensuring patients receive the right treatment at the right time. | Leveraging AI-driven approaches allows for the reallocation of resources from low-value blanket treatment to high-value targeted intervention to optimize patients’ treatment plans. |
Beyond ROI and productivity gains, MMAI models can further support health systems, especially in underserved regions of the world, such as Africa and Asia, where AI-assisted telepathology and teleradiology networks are already bridging diagnostic gaps, reinforcing MMAI’s role in advancing global cancer equity.
Overall, MMAI enhances cost-effectiveness, fosters data-driven reimbursement models, and promotes equitable, sustainable oncology care worldwide.
MMAI can materially improve cancer care, but despite all the progress in the development of MMAI-driven approaches, its adoption is challenged by fragmentation, trust and bias concerns, immature evaluation standards, and equity risks. Amongst the key aspects for ensuring a successful deployment, the authors highlight:
Multimodal AI stands at the forefront of an oncology revolution. By uniting biological, clinical, and digital data, MMAI provides an integrated lens through which cancer can be understood, predicted, and treated more effectively and timely.
Initiatives like ABACO and TRIDENT demonstrate how MMAI can accelerate both real-world learning and clinical validation, shortening the path from data to discovery to patient benefit.
While challenges remain, the convergence of multimodal intelligence, precision medicine, and cross-industry collaboration marks a transformative step toward more predictive, equitable, and sustainable cancer care, at scale.
To learn more about SOPHiA DDM™ for Multimodal and our ongoing collaborations, explore our dedicated webpage.
Disclaimer
SOPHiA DDM™ for Multimodal is a concept in development. May not be available for sale.
SOPHiA GENETICS products are for Research Use Only and not for use in diagnostic procedures unless specified otherwise.
SOPHiA DDM™ Dx Hereditary Cancer Solution, SOPHiA DDM™ Dx RNAtarget Oncology Solution and SOPHiA DDM™ Dx Homologous Recombination Deficiency Solution are available as CE-IVD products for In Vitro Diagnostic Use in the European Economic Area (EEA), the United Kingdom and Switzerland. SOPHiA DDM™ Dx Myeloid Solution and SOPHiA DDM™ Dx Solid Tumor Solution are available as CE-IVD products for In Vitro Diagnostic Use in the EEA, the United Kingdom, Switzerland, and Israel. Information about products that may or may not be available in different countries and if applicable, may or may not have received approval or market clearance by a governmental regulatory body for different indications for use. Please contact us to obtain the appropriate product information for your country of residence.
All third-party trademarks listed by SOPHiA GENETICS remain the property of their respective owners. Unless specifically identified as such, SOPHiA GENETICS’ use of third-party trademarks does not indicate any relationship, sponsorship, or endorsement between SOPHiA GENETICS and the owners of these trademarks. Any references by SOPHiA GENETICS to third-party trademarks is to identify the corresponding third-party goods and/or services and shall be considered nominative fair use under the trademark law.